Joint Pain Relief In San Diego

Causes of poor joint pain:
- Inflammatory diet
- Aging – collagen levels decline with age and make joints more prone to pain and injury
- Arthritis
- Osteoarthritis
- Nutrient deficiencies such as vitamin C, collagen, vitamin D, or magnesium
- Elevated cortisol from chronic stress
- Hormone imbalance i.e. decreased levels of testosterone or estrogen
- Overuse
- Decreased muscle strength
- Incorrect weight lifting form
- Trauma
- Poor posture
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Autoimmune conditions
Symptoms of poor joint health:
- Knee pain when walking up an incline or up stairs
- Elbow pain after playing tennis or golf
- Joint stiffness
- Painful range of motion in joints
- History of repetitive joint injuries i.e. multiple knee injuries or ankle sprains
- History of ligament and tendon tears or sprains
- Joint pain while engaging in daily activity
- Joint pain while engaging in physical exercise or weight lifting
Conventional treatments for joint pain relief
- NSAID drugs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatories) i.e. aspirin, advil, or naproxen
- COX-2 inhibitors (celecoxib)
- Physical therapy
- In severe cases, opioid drugs
Cortisone (injections)

Conditions that can benefit from joint pain relief:
- Osteoarthritis of the knee
- Joint pain stiffness
- Golfers elbow
- Tennis elbow
- Rotator cuff injuries
- Connective tissue injury
- Sports related injuries i.e. ACL and MCL
- Tendinopathy
- Tendonitis
- Meniscal tears

Naturopathic perspective for joint pain relief
Timely treatment of joint pain is essential in order to mitigate the damage it can cause. Additionally, research has found that increased body weight puts more stress on the load-bearing joints which increases the risk of developing joint issues. The link between obesity and osteoarthritis has been established by numerous studies, leading many joint pain relief programs to focus on reducing body weight to reduce the strain on the hips, knees, and ankles.
- Joint protection
- Exercise
- Maintenance of healthy body weight
- Strengthen balance
- Strengthen muscles
- Calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D
- Anti-inflammatory diet
- Anti-inflammatory nutraceuticals and herbs
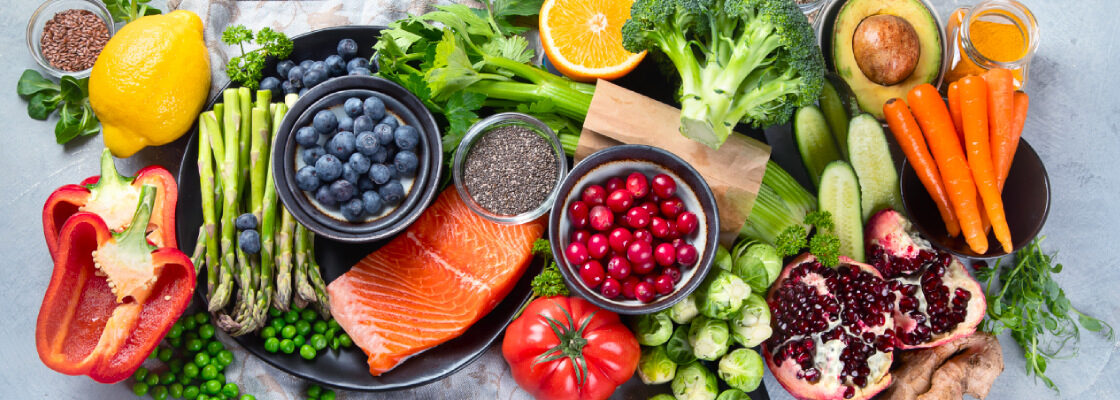

Anti-inflammatory Diet
A poor diet is a leading contributor to inflammation in our society. High levels of inflammation can wreak havoc in the body, adding to pain and causing tissue damage. Meat and milk are known for producing inflammatory prostaglandins. Joints are especially sensitive to inflammation, so adopting an anti-inflammatory diet is one of the best ways to promote good joint health.
Certain foods high in Omega-3 fatty acids, such as SMASH fish, walnuts, and chia seeds, can help reduce inflammation levels in the body.
Consuming fewer processed foods, sugars, and trans fats can help reduce inflammation in the body.
Hormone Balancing
Joint pain can be a symptom that results from declining estrogen levels, as estrogen has an anti-inflammatory effect on the body.
Increased cortisol from chronic stress can lead to increased joint pain
Research has demonstrated that testosterone can support weight, disc, and tendon health, as well as reduce inflammation levels such as TNF-alpha, IL-1B, IL-6, and CRP.
Losing weight if needed
Excess body weight can lead to increased joint pain and injury due to the strain it puts on joints. In addition, excess body fat is inflammatory, which as previously mentioned can cause a number of issues for joints.
PRP
PRP (platelet rich plasma) is a great choice for numerous joint-related issues. This method is straightforward and uses the body’s natural healing properties to begin the joint recovery process. PRP has potential long-term recuperative advantages, and we generally observe a 60-80% improvement rate in our patients.
For more about PRP, check out our article here (link to PRP blog here)
Prolotherapy
Prolotherapy is comparable to PRP and involves injecting a combination of dextrose and saline into the affected joint to trigger the healing response.
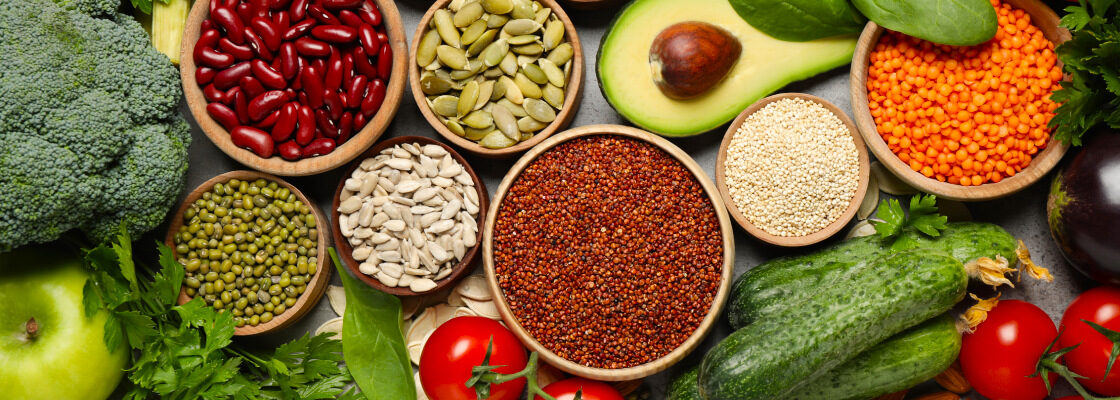

Nutrients for joint health:
Curcumin
Curcumin is known to have anti-inflammatory effects comparable to hydrocortisone. It works by inhibiting NF-KB as well as COX and LOX enzymes, leading to a decrease in leukotrienes and prostaglandins which contribute to inflammation. Stimulates regeneration of muscle and tissue repair
Ginger
Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory
Boswellia
Anti-inflammatory and works by inhibiting 5-lipoxygenase, the enzyme that controls the production of leukotrienes. Can be beneficial for the treatment of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Collagen
Keeps cartilage healthy so joints have proper cushioning. Shown to support healthy joints by reducing stiffness and pain.
Vitamin C
Is essential in collagen production in the body. Enzymes dependent on Vitamin C combine proline and glycine to initiate collagen synthesis.
Vitamin D
Major role in the inflammatory response and has been shown to decrease proinflammatory cytokines i.e. IL-12, IL-6, CRP, TNF-alpha as well as reduce pain. Calcium absorption is highly dependent on healthy vitamin D levels.
Magnesium
Most people are deficient in magnesium, and a deficiency in magnesium can lead to increased levels of inflammation and increased risk of joint pain.
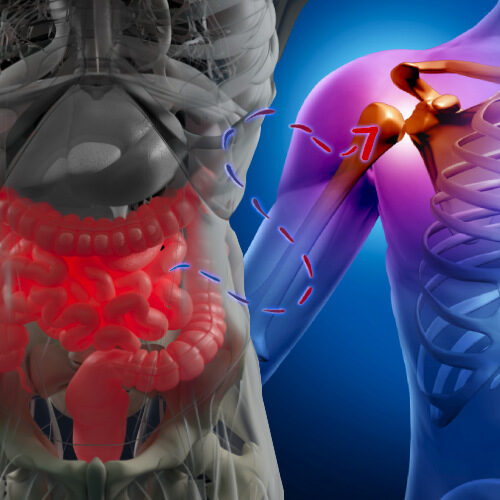
What is arthritis?
The term ‘arthritis’ refers to joint inflammation, with the individual exhibiting symptoms such as stiffness, swelling and pain. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are the two most common forms of arthritis.
Uncovering the root cause of immune dysregulation is a key part of naturopathic and functional medicine when it comes to treating joint pain, and is like peeling back layers of an onion in order to identify the true source of the pain.
The gut-joint axis
The antigens found in the gut from pathogens, bacteria, and certain proteins can lead to tissue inflammation and joint dysfunction. Bacterial toxins known as lipopolysaccharide (LPS) are able to trigger the production of inflammatory cytokines which may contribute to the development of arthritis-like symptoms.
